Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF), also known as Polyvinylidene Difluoride, mainly refers to vinylidene fluoride homopolymer or copolymer of vinylidene fluoride and other small amounts of fluorine-containing vinyl monomers. Therefore, PVDF resin has the characteristics of both fluororesin and general resin. As a non-polar chain polymer, PVDF resin has a molecular weight generally greater than 300,000. The application of PVDF is mainly concentrated in architectural coatings, water treatment membranes, lithium battery binders and diaphragms. In addition to good chemical corrosion resistance, high temperature resistance, oxidation resistance, weather resistance, and radiation resistance, polyvinylidene fluoride also has special properties such as piezoelectricity, dielectricity, and thermoelectricity. It is currently the second largest polymer in terms of output among fluorine-containing plastics.
Main Applications of Polyvinylidene Difluoride PVDF in Lithium Batteries
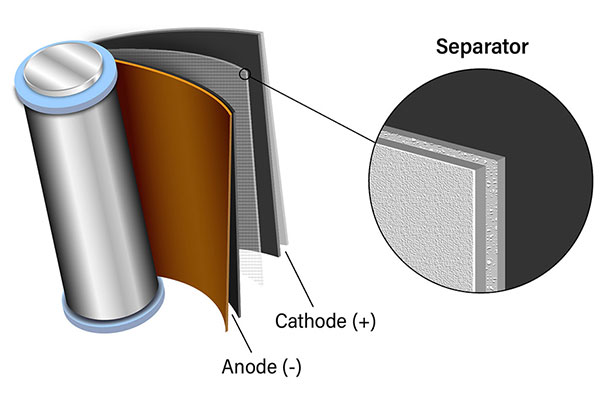
PVDF powder is mainly used as a positive electrode binder and diaphragm coating material in lithium batteries.
Firstly, as a positive electrode binder, PVDF can connect positive electrode active materials, conductive agents, and current collectors, thereby reducing electrode impedance and battery polarization.
Due to its strong high-voltage resistance, good thermal stability and easy dispersion, PVDF is the most commonly used oily positive electrode binder, accounting for about 90% of the market share. In contrast, water-based binders have a smaller market share due to their poor high-voltage resistance, damage to positive electrode materials and difficulty in drying. With the rapid development of high-voltage and high-energy-density battery systems, high-voltage stability has become an important indicator of binders. Therefore, compared with water-based binders, PVDF resin with a wide electrochemical window is more irreplaceable.
| Property | Unit | DS202B | DS202D | DS202E | Testing Method |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Appearance | / | White Powder | White Powder | White Powder | / |
| Smell | / | NO | MO | NO | / |
| Melting Point | ℃ | 156-165 | 156-165 | 156-165 | GB/T 28724 |
| Thermal Decomposition Temperature,> | ℃ | 380 | 380 | 380 | GB/T 33047 |
| Relative Density | / | 1.75-1.79 | 1.75-1.79 | 1.75-1.79 | GB/T 1033 |
| Moisture Content, ≤ | % | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.10 | GB/T 6284 |
| Rotary Viscosity | mpa·s | 8500-22000 | 1000-4000 | 2000-5000 | 30℃ 0.1g/gNMP (DS202B), 30℃ 0.07g/gNMP (DS202D & DS202E) |

Performance requirements of lithium battery grade PVDF Resin
1. High viscosity. In order to increase the energy density of the battery, a small amount of PVDF is required when using it as a lithium battery binder, usually between 1.5% and 4%. Therefore, lithium battery grade PVDF needs to have a higher bonding force, that is, a higher molecular weight.
2. Molecular weight consistency. Lithium battery grade PVDF needs to have a very high molecular weight consistency, which requires a high-precision reactor and advanced reaction process control technology.
3. High purity. Impurities in battery operation will interfere with the electrochemical reaction, thereby affecting the battery life.
4. High flexibility. During the production process, the battery is subjected to a lot of mechanical pressure, so the binder needs to maintain bonding force without cracking after the battery is bent.
